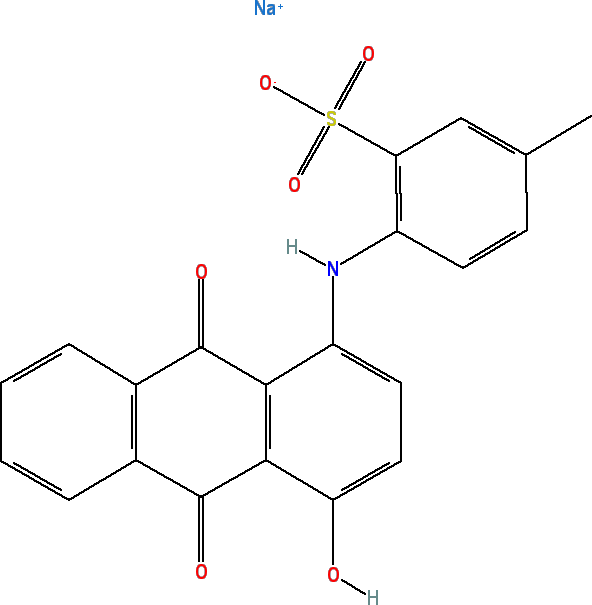
Acid Violet 43
Safety Information
Batches of acid violet 43 that are certified to meet the specifications of the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) are called Ext. violet 2. The FDA allows Ext. violet 2 to be used to color externally applied cosmetics and personal care products when it conforms to FDA specifications. Please search for Ext. violet 2 on this website for more information about this colorant. The safety of acid violet 43 has been assessed by the Expert Panel for Cosmetic Ingredient Safety. The Expert Panel evaluated the scientific data and concluded that acid violet 43 was safe for use in hair dye formulations when impurities were minimized.
Oral toxicity tests do not demonstrate significant acute toxicity. In a short-term dermal toxicity study and a subchronic dermal toxicity study, no signs of systemic toxicity and no significant local skin reactions were noted. This ingredient was not genotoxic in bacterial assays, nor was it carcinogenic when applied to skin at a 1% concentration. Accordingly, acid violet 43 was determined to be safe for use in hair dye formulations, with limitations on impurities.
More information about the safety of hair dyes.
In the European Union, Acid Violet 43, as CI 60730, may be used to color cosmetic products, with the exception of products intended to come in contact with mucous membranes (see Annex IV).